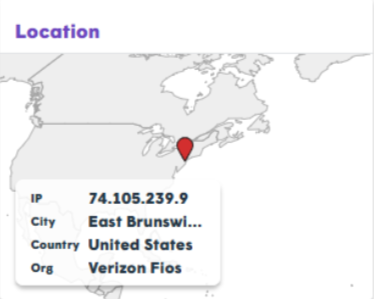
The Location Widget determines a user's geolocation using the public IP address assigned to their browser. This data helps technical teams verify if a user is connecting from a supported region and identifies network pathing that might impact call quality.
Data Collection & Accuracy
| Data Point | Definition & Accuracy |
|---|---|
| IP Address | The public-facing IP where the request originates. |
| City | Converted via GeoIP service. Accuracy: 50–75%. |
| Country | Converted via GeoIP service. Accuracy: 95–99%. |
| Organization | The ISP, carrier, or corporation that owns the IP block. |
Signaling vs. Media Location
During a TytoCare session, the test may observe two different IP addresses:
- Signaling (HTTPS): Used for call setup and control.
- Real-Time Media: Used for the actual video/audio stream.
Why would they differ?
- VPN Routing: A VPN might route standard web traffic (signaling) through the tunnel while "split-tunneling" media directly to the internet.
- IPv6 Coexistence: Signaling may use an IPv6 address, while media servers only support IPv4.
Diagnostic Insights
- Location Mismatch: If the detected location is significantly far from the user's actual location, it often indicates the use of a VPN or HTTP Proxy.
- Quality Degradation: Proxies and VPNs introduce extra "hops," increasing latency. If a proxy is located in a different country, media quality will drop significantly due to the increased travel distance of the data packets.
Support Tip: When troubleshooting "laggy" video, check if the Organization field lists a known VPN provider (e.g., NordVPN, Zscaler). Disabling the VPN usually resolves the issue immediately.




